Share now
Pakistan Flag

Pakistan State Emblem

Map of Pakistan
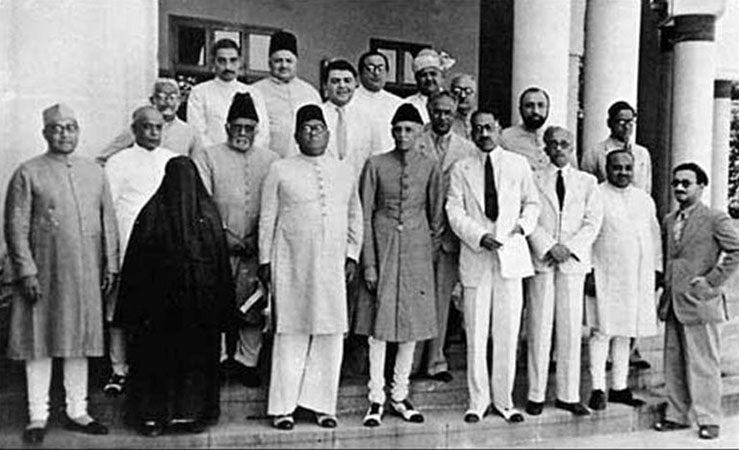
The Pakistan Muslim League Working Committee 1940

Founder of Pakistan Quaid-e-Azam Muhammad Ali Jinnah

Pakistan Introduction
Pakistan was declared a new, independent Nation State by the British Empire at midnight on August 14, 1947; the newly-formed country’s borders were drawn such that the State had two “wings”: one containing provinces to the West of India (West Pakistan) and the second in its East (East Pakistan), leaving independent India in between, literally dividing the two “wings” of the new autonomous country. The word “Pakistan” literally means “Land of (the) Pure” in Urdu and Persian. This name was chosen for the country during the pre-Partition Independence Movement[1], when Choudhary Rahmat Ali, a Pakistan Movement activist, published this name in his pamphlet “Now or Never” in 1934. This name was widely accepted as a name for the new country long before its formation. It was adopted as its official name in August 1947 and officially changed to Islamic Republic of Pakistan in the country’s 1956 Constitution. Pakistan’s East Wing became independent in 1971, after a separationist movement, resulting in Pakistan’s current boundaries.
Pakistan: Geographical Details
Pakistan is located between 23° 42” to 36° 55Ꞌ North latitudes and 60° 45Ꞌ to 75° 20Ꞌ East longitudes. It has a 1,046 km (650 mi) long coastline along the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman in the South, and is bordered by Afghanistan and Iran in the West, India in the East, and China in the far Northeast. Tajikistan is also very close to Pakistan, but is separated by the narrow Wakhan Corridor. Strategically, it is located in the important regions of South Asia, Central Asia, and the Middle East.
Pakistan at a Glance
| Name of Country | Islamic Republic of Pakistan | |||||
| Capital/Headquarter | Islamabad | |||||
| Population[2] | 207,775,000 persons | |||||
| Area[3] | 796,095 km2 | |||||
| Population Density | 261.0 persons per km2 | |||||
| Population Growth Rate[4] | 2.4% | |||||
| Male Population[5] | 51.2% | |||||
| Female Population[6] | 48.7% | |||||
| Urban Population[7] | 36.4% | |||||
| Literacy Rate[8] | 60% | |||||
| Male Literacy Rate[9] | 70% | |||||
| Female Literacy Rate[10] | 49% | |||||
| Administrative Units | 4 provinces and 121 districts and one Territory. The districts are further divided into tehsils/ talukas and Union Councils. Islamabad is the Capital Territory | |||||
| Provinces/ Districts | Provinces | Districts | ||||
| Sindh | 23 districts, | |||||
| Punjab | 36 districts | |||||
| Khyber Pakhtunkhwa | 32 districts | |||||
| Balochistan | 30 districts | |||||
| Territories/ Districts | Territories | Districts | ||||
| Islamabad Capital Territory | 1 | |||||
| Gilgit-Baltistan (G-B) | 7[11] | |||||
| Azad Kashmir (AK) | 10 | |||||
| Major Cities | Karachi (Capital of Sindh), Lahore (Capital of Punjab), Peshawar (Capital of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa), Quetta (Capital of Balochistan), Islamabad (Pakistan’s Capital), Faisalabad (Punjab), Hyderabad (Sindh), Ziarat (Balochistan), Larkana (Sindh), Rawalpindi (Punjab), Multan (Punjab), Gujranwala (Punjab), and Thatta (Sindh) | |||||
| Size of Economy[12] | 26th largest economy of the world based on its purchasing power | |||||
| Major Economic Activity[13] | Major contributors to the Gross Domestic Production (GDP) of Pakistan include: | |||||
| Agriculture | 18.5% | |||||
| Industry | 13.8% | |||||
| Services | 56.0% | |||||
| Main Crops[14] | Wheat, rice, sugarcane, cotton, seed oil, barley, mustard, maize, oats, bajra, jowar, gram, pulses, groundnut (peanut), soya bean, tobacco, sesanum, guarseed, sunhemp, jute, linseed, rapeseed, mustard and other oil seeds, and tobacco | |||||
| Major Fruits | Melon, banana, dates, guava, jaamun, mango, watermelon, musk melon, papaya, phalsa, citrus, ber, mulberry, apple, coconut, chikoo, grapes, peach, pear, plum, pomegranate, almonds, and walnuts | |||||
| Major Vegetables | Okra, tinda, brinjal, bitter gourd, bottle gourd, pumpkin, melon pumpkin, luffa, cucumber, long melon, arum, beans, lotus root, turnip, carrots, radish, spinach, tomatoes, cauliflower, cabbage, sweet potato, peas, garden peas, fenugreek, lettuce, sugar beet, chilies, garlic, coriander, ajwain, and fennel | |||||
| Forests (Area)[15] | 4.47 million HA | |||||
| Total Roads[16] | 268,935 km | |||||
| Total Black Topped Roads[17] | 197,452 km | |||||
| Low Type Roads[18] | 714,83 km | |||||
|
Electricity Production[19]
|
Type | Installed Capacity | Dependable Capacity | |||
| WAPDA Hydro | 9,417 MW | 8,143 MW | ||||
| IPPs Hydro | 372 MW | 372 MW | ||||
| GENCOs with PEPCO[20]s | 5,637 MW | 5,637 MW | ||||
| IPPs with PEPCO | 16,946 MW | 16,297 MW | ||||
| Others with PEPCO | 340 MW | 340 MW | ||||
| Nuclear | 1,330 MW | 1,330 MW | ||||
| Karachi Electric | 3,084 MW | 2,884 MW | ||||
| Wind/Bagass/Solar | 2,047 MW | 1,779 MW | ||||
| Total | 39,145 MW | 35,980 MW | ||||
| Telecommunications |
The Telecommunications system in Pakistan consists of Microwave Radio Relay, coaxial cable, fiber optic cable, cellular, and satellite networks. 90% of Pakistan has cellphone coverage, and more than half of all Pakistanis have access to a cell phone; fiber optic systems are being constructed throughout the country to aid in network growth. |
|||||
| Industrial Estates/Zones | Total Industrial Estates | 77 | ||||
| Sindh | 28 | |||||
| Punjab | 27 | |||||
| Khyber Pakhtunkhwa | 12 | |||||
| Balochistan | 7 | |||||
| Federal Capital Area | 3 | |||||
| Major Industry | Textile & apparel, food processing, pharmaceuticals, construction materials, chemicals, cement, mining, machinery, steel engineering, computer software & hardware, automobiles, motorcycles, auto parts, electronics, paper & paper products, fertilizers, sugar, defense products, shipbuilding and ship breaking, transport equipment, beverages, sport goods, sugar, and tobacco | |||||
| Household Size[21] | 6.45 persons per household | |||||
| Houses with Piped Water Inside[22] | 34.5% | |||||
| Houses with Electricity[23] | 91% | |||||
Table 1.1 Pakistan at a Glance
[1] For details of Pakistan’s history, including details about the Independence movement, see section: Pakistan History.
[2] Sindh Development Statistics 2018
[3] 1998 Census; 2017 Census uses spatial data.
[4] Census of Pakistan 2017
[5] Census of Pakistan 2017
[6] Census of Pakistan 2017
[7] Census of Pakistan 2017
[8] Pakistan Social & Living Measurement Survey 2018-19 (PSLM)
[9] PSLM 2018-19
[10] PSLM 2018-19
[11] Gilgit Baltistan and Azad Kashmir are disputed territories and thus even though controlled by Pakistan Government these have not been considered part of Pakistan.
[12] Pakistan Economy 2018, CIA World Fact Book
[13] Pakistan Economic Survey 2018-19
[14] For details about what is produced where, please see chapters/ volumes on individual provinces and districts. I have used local names for crops, fruits, and vegetables indigent to the region.
[15] Agriculture Statistics of Pakistan 2017-2018
[16] Pakistan Statistical Yearbook 2018 (PSY)
[17] PSY
[18] PSY
[19] State of Industry Report 2019, By National Electric Power Regulatory Authority (NEPRA) From NEPRA Official Website
[20] PEPCO stands for Pakistan Electric Power Company and is a ivisio of water & Power Ministry
[21] Pakistan 2017 Census
[22] 2017 Census
[23] PSLM 2017-18
